Chlamydia: Understanding, Testing, and Treatment
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is one of the most common STDs, affecting millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, chlamydia often goes undiagnosed because it frequently causes no symptoms. However, left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health complications, emphasizing the importance of regular testing and prompt treatment.
Understanding Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection spread through sexual contact. It can infect the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body), cervix, rectum, and sometimes the eyes and throat.
Symptoms of Chlamydia While many people with chlamydia have no symptoms, some may experience:
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Bleeding between periods
- Testicular pain
- Rectal pain
The Importance of Chlamydia Testing
Regular chlamydia testing is crucial for several reasons:
- Early Detection Early detection allows for prompt treatment, preventing complications and reducing the risk of spreading the infection.
- Preventing Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Untreated chlamydia can spread to the reproductive organs, causing PID, a serious infection that can lead to infertility and ectopic pregnancy.
- Partner Notification If diagnosed with chlamydia, it is important to inform previous sexual partners so they can also get tested and treated.
Who Should Get Tested for Chlamydia?
Anyone who is sexually active should consider getting tested for chlamydia regularly. People at higher risk include:
- Those with multiple sexual partners
- Those who have had a new sexual partner
- Those who have been diagnosed with another STD
Chlamydia Testing Methods
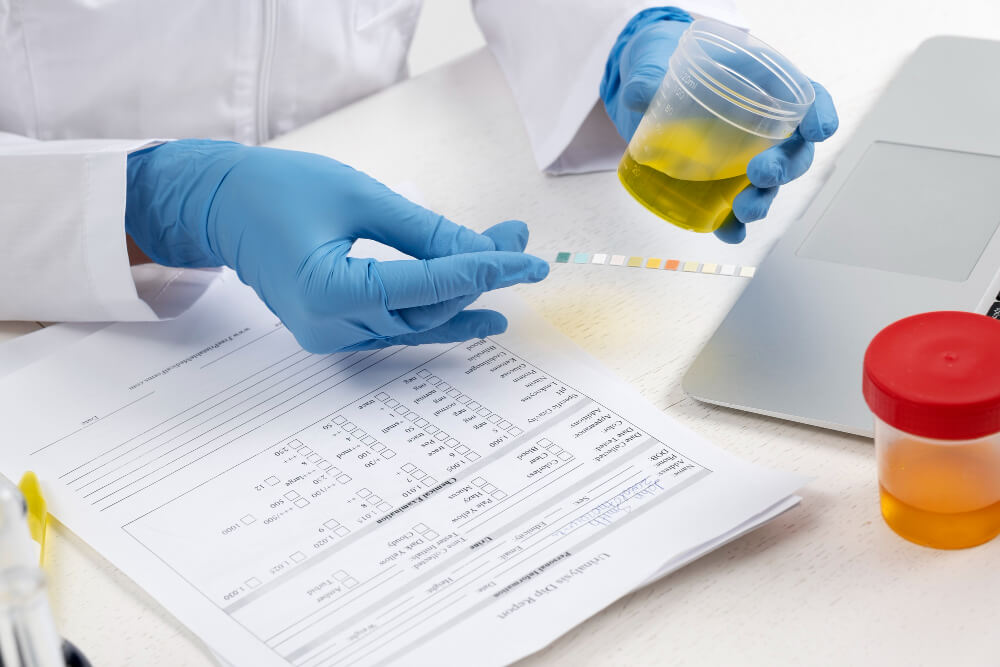

Several methods are available for chlamydia testing:
- Urine Test A common and non-invasive method involving a urine sample.
- Swab Test A swab is used to collect a sample from the urethra, cervix, rectum, or throat.
- At-Home Tests Over-the-counter chlamydia tests are available in some regions.
Chlamydia Treatment
Chlamydia is treatable with antibiotics:
- Treatment Options Azithromycin and doxycycline are commonly prescribed antibiotics.
- Partner Notification Sexual partners should also be tested and treated to prevent reinfection.
- Follow-Up It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics and schedule a follow-up test to confirm the infection is cleared.
Preventing Chlamydia
Reducing the risk of chlamydia involves:
- Consistent Condom Use Using condoms correctly and consistently during sexual intercourse.
- Limiting Sexual Partners Reducing the number of sexual partners can lower the risk of exposure.
- Getting Vaccinated The HPV vaccine can help protect against certain types of HPV, which can increase the risk of chlamydia infection.
Regular chlamydia testing is crucial for preventing the spread of infection and avoiding potential health complications. Early detection and treatment are key to maintaining sexual health and well-being.
